A look at how postgREST does joins and the gotchas involved
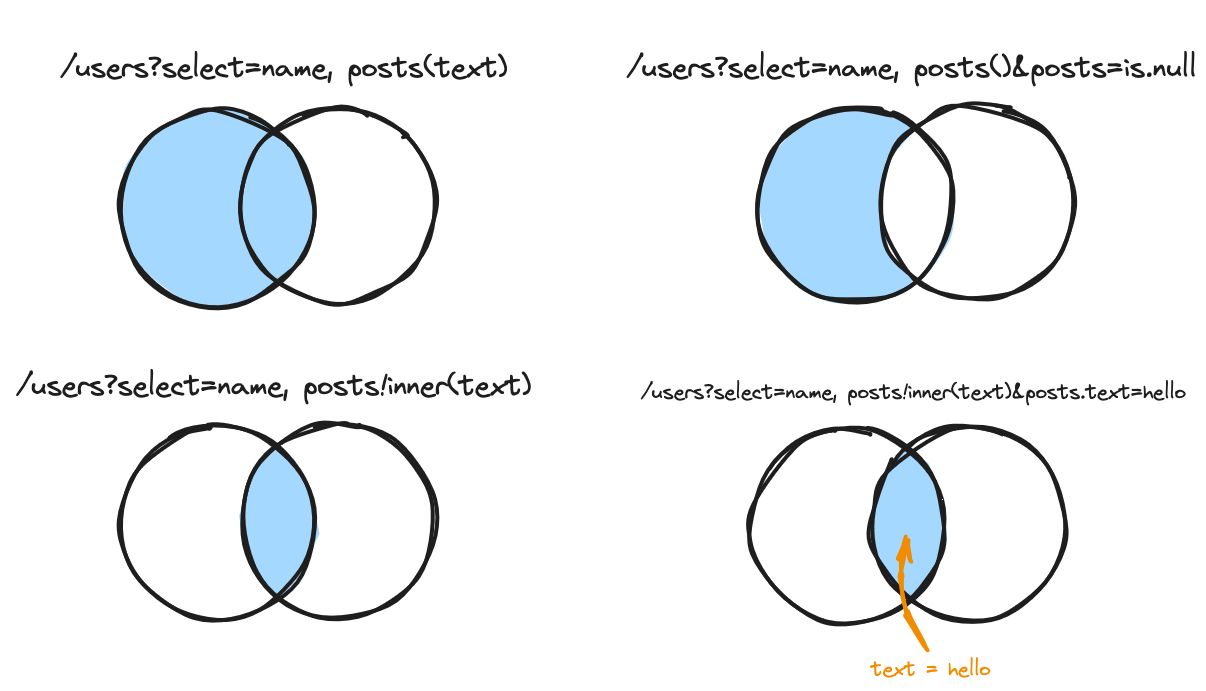
Unspecified: left joins
PostgREST
Supabase/postgrest-js
GET /users?select=name,posts(text)A regular PostgREST embed.
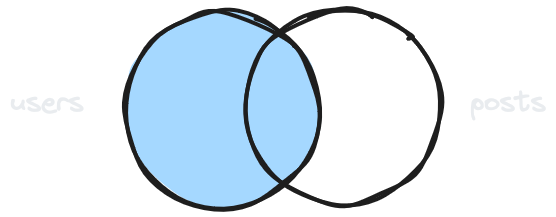
!inner for inner joins
PostgREST
Supabase/postgrest-js
GET /users?select=name,posts!inner(text)Only include rows that exist in both tables.
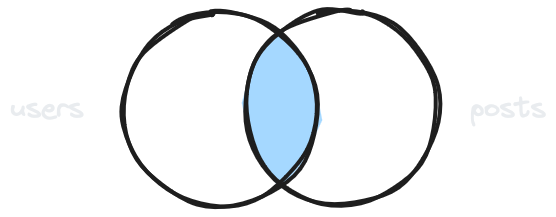
Left join with condition
PostgREST
Supabase/postgrest-js
GET /users?select=name,posts(text)&posts.text=helloFilters results in the embedded table (posts). Importantly, this will not filter the top-level users at all. Use inner joins with conditions for that.
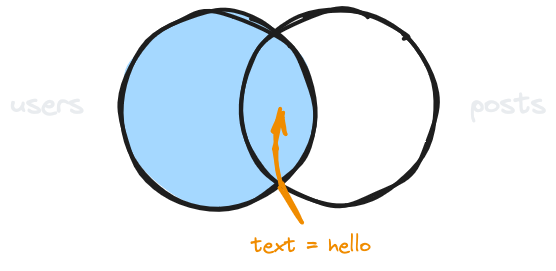
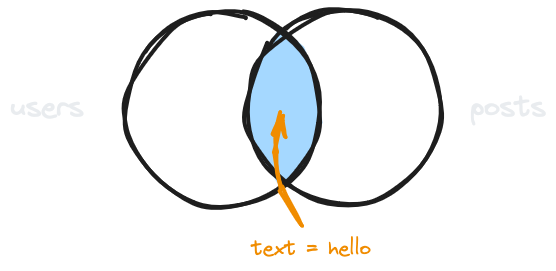
Inner join with condition
PostgREST
Supabase/postgrest-js
GET /users?select=name,posts!inner(text)&posts.text=helloFilters results in the embedded table (posts) while also only keeping users that have at least one embedded post.
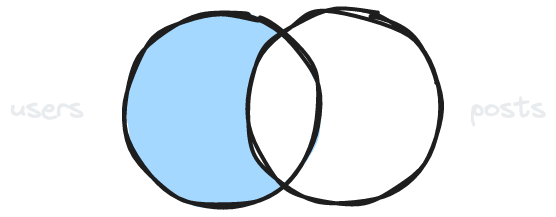
Null condition for anti-joins
PostgREST
Supabase/postgrest-js
GET /users?select=name,posts()&posts=is.nullSkip users for which there exists a post.
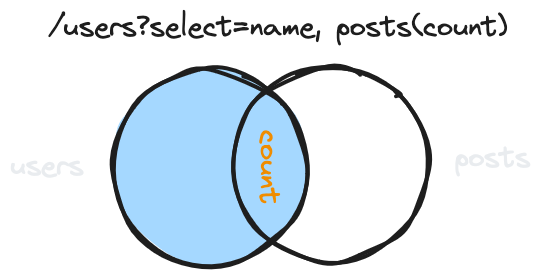
count for an embedded resource count
PostgREST
Supabase/postgrest-js
GET /users?select=name,posts(count)When count is the only column for an embedded resource, PostgREST returns the number of items in the relationship.
While this cannot be directly combined with actually returning embedded relationships data, you can embed the same table twice:
PostgREST
Supabase/postgrest-js
GET /users?select=name,posts(text),post_count:posts(count)